EU’s New Crypto Transaction Tracing Requirements to Bring Major Change to the Industry
On Tuesday, the EU Council of Ministers approved a regulation that requires the transmission of information for money transfers and cryptocurrencies, effectively banning anonymous crypto wallets and extending due diligence requirements such as identification requirements to the entire sector.
This move is a major step forward in the fight against money laundering and terrorist financing, making it much harder for criminals to use crypto assets to anonymously move money around the world.
The regulation, which was recently approved by the EU Parliament, aims to make the transfer of crypto assets “fully” traceable, creating a more secure and trusted environment for legitimate users and is expected to have a positive impact on the crypto market, as it will help to create a more secure, trusted environment for legitimate users. The regulation is expected to come into force in 2024. Here are some of its key provisions:
- Ban on anonymous crypto wallets: The regulation will ban the use of anonymous crypto wallets. This will make it more difficult for criminals to use crypto assets to anonymously move money around the world.
- Due diligence requirements: The regulation will extend due diligence requirements to the entire crypto sector. This means that crypto service providers will be required to identify their customers and verify their identity.
- Traceability requirements: The regulation will require crypto service providers to keep records of all crypto transactions. This will make it easier for law enforcement to track down criminals who use crypto assets for illegal activities.
Initially, the EU proposed a €1,000 transaction limit for crypto assets in its draft regulation in order to preserve the efficiency of the payment system. However, European Members of Parliament (MEPs) and representatives of EU member states rejected this limit. As a result, all transfers of crypto assets must now contain information about the source and recipient. This information must be made available to the competent authorities.
In principle, the regulations also apply to transactions with “unhosted wallets.” Unhosted wallets are not managed by intermediaries, such as exchanges or crypto asset service providers. They are the basis for decentralized financial applications.
However, there are a few special provisions for unhosted wallets. Following are some of the special provisions for unhosted wallets:
- The regulations do not apply to transactions between unhosted wallets.
- The regulations do not apply to transactions where the value is below a certain threshold.
- The regulations do not apply to transactions where the sender and recipient are known to each other.
The EU’s new crypto regulations are a significant step towards regulating the crypto market. The regulations are expected to make it more difficult for criminals to use crypto assets for illegal activities. They are also expected to protect consumers and investors.
Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA)
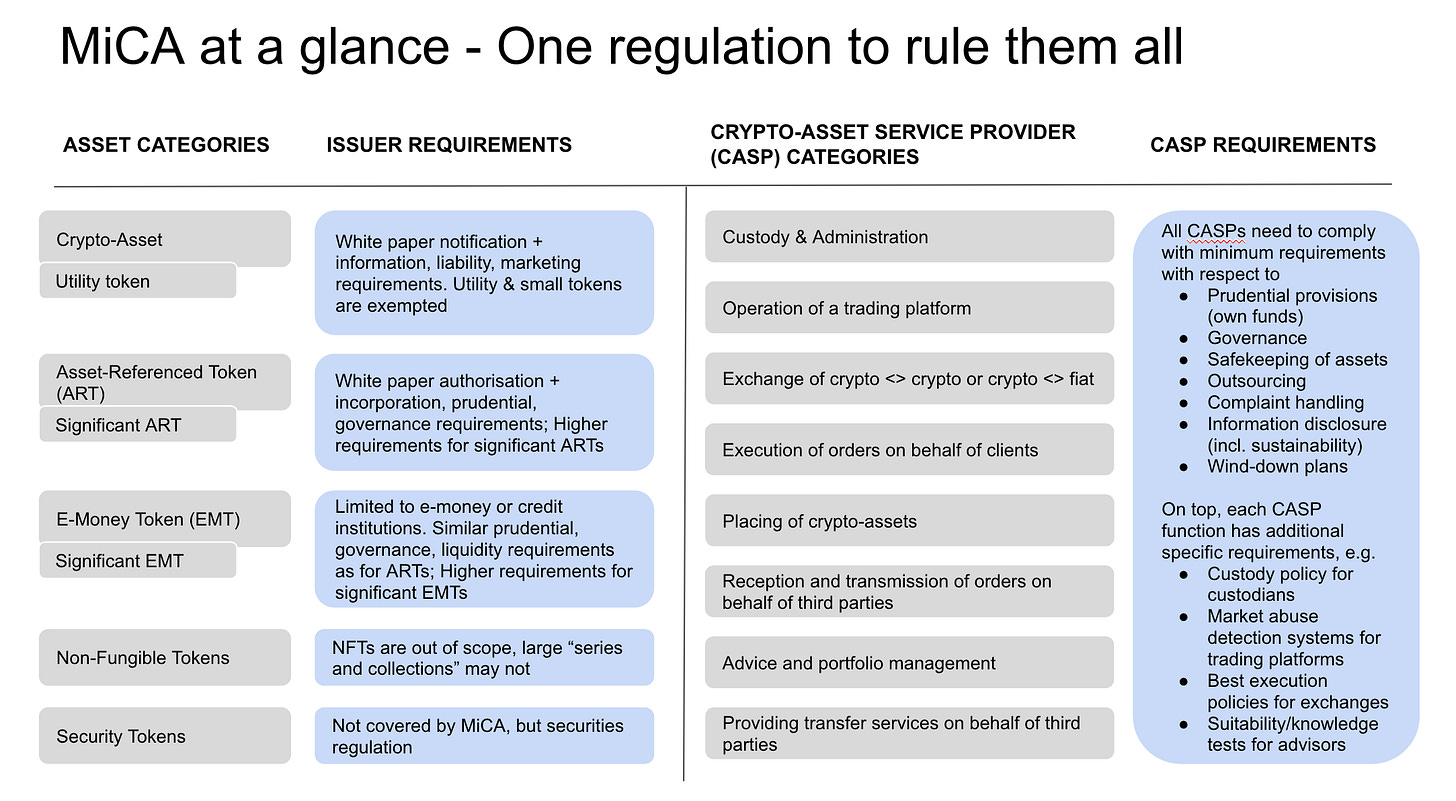
The Council also gave its final approval to the new regulation on Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA). Its provisions are intended to protect consumers and investors from abuse and manipulation on volatile crypto marketplaces as well as to ensure financial stability.
Under MiCA issuers of stablecoins, such as Tether or Circle’s USDC, will be required to build up a sufficiently liquid reserve in the ratio 1:1 and partly in form of deposits, intended to prevent total defaults and ensure that stablecoins are always backed by assets of equivalent value.
Under the new rules, stablecoin issuers will be required to have a physical presence in the EU and to hold sufficient reserves to back their tokens. They will also be subject to strict capital and liquidity requirements.
In addition, the regulations will limit the amount of stablecoins that can be traded each day to 200 million euros. This is intended to prevent stablecoins from being used for speculative trading or money laundering.
The new rules are seen as a way to protect consumers and investors from the risks associated with stablecoins. They are also expected to help to promote the development of a stable and reliable crypto-asset market in the EU.
Here are some additional details about the new regulations:
- Stablecoin issuers will be required to have a minimum capital of €3 million.
- They will also be required to hold reserves that are at least equal to the value of the stablecoins they issue.
- Stablecoins will be subject to the same anti-money laundering and terrorist financing regulations as other financial products.
- The European Banking Authority (EBA) will be responsible for supervising stablecoin issuers.
MiCA also includes a number of other provisions designed to protect consumers and investors, such as requiring crypto service providers to conduct due diligence on their customers and to keep records of all transactions.
In a statement, EU Financial Services Commissioner Mairead McGuinness said that MiCA is “a historic moment for the EU and for the global crypto-asset sector.” She added that the regulation will “create a level playing field for all market participants, while ensuring consumers and investors are protected.”
MiCA’s approval is a significant step forward for crypto market regulations in the EU and is expected to bring greater security and trust to the market, as well as making it more difficult for criminals to use crypto assets for illicit activities.
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, will be excluded from MiCA. NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of real objects, such as art, music, and videos. They are not considered to be crypto assets under the MiCA framework.
Swedish Finance Minister Elisabeth Svantesson welcomed the conclusion of the two legislative procedures, saying that it is urgent to “prevent the misuse of the crypto economy for the purpose of money laundering and financing terrorism.”
She also said that today’s decision is “unwelcome news for those who misuse crypto assets for illegal activities to circumvent EU sanctions and finance war.”
Both regulations can now enter into force after their publication in the Official Journal of the EU. They will then take effect a short time later and no longer need to be transposed into national law.
Source: paddihansen.substack.com
EU Finance Ministers Finalize Reforms of Crypto Assets Taxation
EU finance ministers have also taken a position on the reform of the directive on administrative cooperation in the field of taxation. This is primarily concerned with the reporting and automatic exchange of information on income from transactions with crypto assets and on advance rulings for the particularly wealthy.
The scope of the previous registration and reporting obligations and the general cooperation of the tax authorities are to be expanded. This includes all crypto assets such as stablecoins, e-money tokens, and certain NFTs.
In order to close loopholes, especially in the case of bitcoins that can be traded across borders, tax authorities will be obliged to automatically exchange information, such as the tax identification number, that providers of crypto services must provide. Parliament can still comment on this planned “DAC 8” directive, but it will have no say in the matter. The Commission praised the fact that users who made profits with crypto assets would no longer remain “under the radar of national tax authorities thanks to anonymity.”
Further sources:
www.kiratas.com/2022/06/30/bitcoin-co-eu-bodies-agree-to-end-anonymous-crypto-payments/


Decentralization + Security + Anonymity are the most vital features of the crypto & blockchain communities. If we centralize it using the same mechanisms, then what makes crypto different vs FIAT? Only inflation rate? MICA Act overall is fine piece of legislation, with few minor weaknesses that hopefully the EU addresses soon and closes those gaps. The US is way behind in the regulatory process.