With its ability to securely store and manage digital records, Blockchain has enabled businesses to conduct transactions with greater security, accuracy, and transparency than ever before. Moreover, its ability to store and manage data cost-effectively has enabled businesses to gain valuable insights from their data. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its potential to transform the way we do business and manage data is becoming increasingly clear.
Blockchain Statistics
Data provenance has been identified as the top use case for blockchain, with PricewaterhouseCoopers (2020) estimating that it will contribute $962 billion to global GDP by 2030. It’s followed by payments and finance ($433 billion), identity ($224 billion), contracts and dispute resolution ($73 billion), and customer engagement ($54 billion).
A Deloitte survey of senior executives from around the world has found that 39% of them have adopted blockchain technologies in their organizations. Of those companies, 41% had a revenue of more than $100 million and 46% had a revenue of more than $1 billion. (Deloitte, 2020) The survey indicates that the technology is being embraced by larger companies.
Blockchain’s potential applications go far beyond the financial sector. It is being used and tested in a variety of industries, from healthcare to transportation, to help securely store and transfer data. In terms of blockchain spending, the professional services industry is predicted to have the fastest growth with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 54%., followed by government (48.2%) and healthcare (43.9%).
Most Prominent Blockchain Use Cases
From contact tracing to patient record sharing, the applications of blockchain technology are growing, and with them, so is the data. The most prominent use of blockchain, however, is in the financial sector, where the technology has enabled the development of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, Algorand, XRP and many more.
Blockchain in Financial Services
According to IDC, the banking industry has spent the most on blockchain technology in 2020, with a total of 29.7%
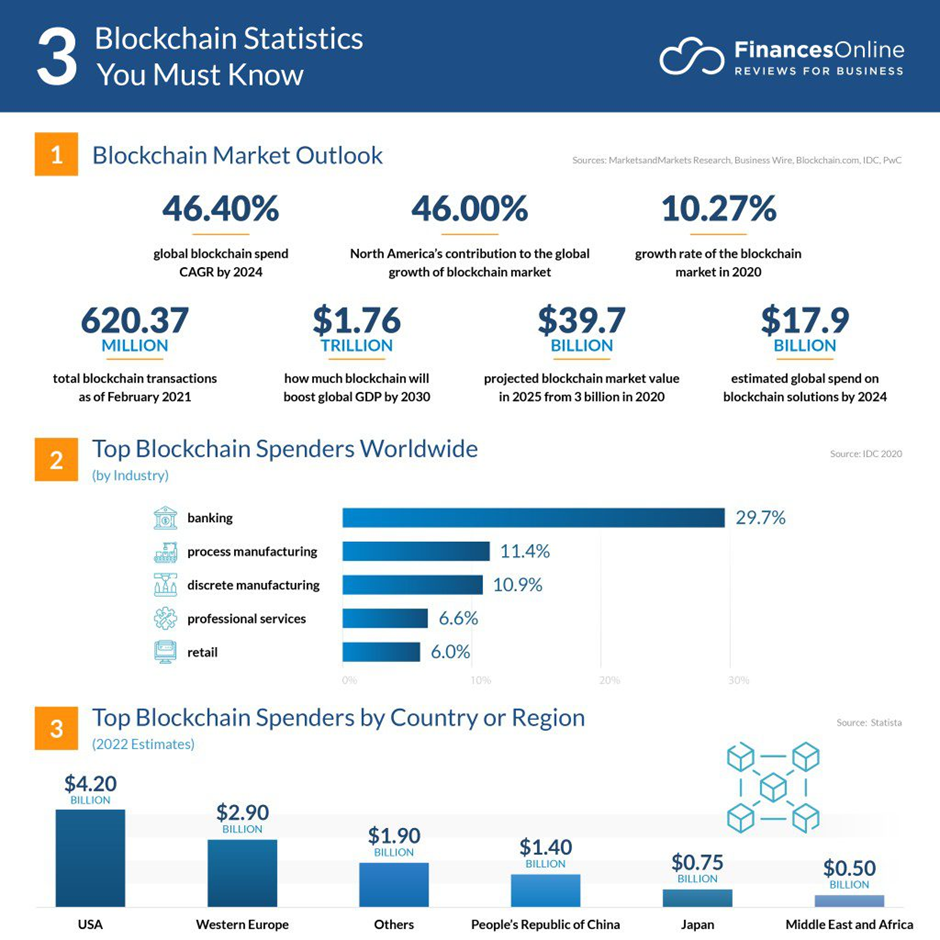
Source: Statista/FinancesOnline
By enabling faster and more secure transactions, it has become the go-to choice for many financial services companies. A recent survey conducted by Deloitte found that 95% of these companies are exploring how to incorporate blockchain technology into their operations – a testament to the power of blockchain technology’s decentralized nature, which allows for near-instantaneous transactions that are difficult to manipulate.
As blockchain technology continues to grow in popularity and its potential becomes more widely understood, its impact on the financial sector is likely to be far-reaching.
International payments – faster and cheaper cross-boarder payments:
- For example Ripple, a blockchain-based payment network, that allows for near-instant and low-cost international payments, has partnered with a number of banks and financial institutions around the world, and is currently used by over 300 financial institutions to send and receive money internationally.
- The global payment network SWIFT that is used by over 11,000 financial institutions around the world is currently exploring the use of blockchain technology to improve the speed, efficiency, and security of its payments network.
Capital markets – more efficient and transparent:
- For example, the Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) is using blockchain technology to create a new platform for clearing and settling securities transactions. This new platform, called Project Ion, is designed to be more efficient, transparent, faster, cheaper and more secure than the current system in use.
Trade finance – more efficient, transparent and secure:
- For example, TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform that is used to track the movement of goods across the supply chain, is a joint initiative of IBM and Maersk, and currently used by over 90 organizations around the world.
Regulatory compliance and auditing – improved systems to reduce fraud and errors, save banks time and money:
- For example, Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain framework used by banks to track and manage their compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and allows banks to share information about suspicious transactions with each other, which can help to identify and prevent money laundering.
Blockchain in Healthcare
The potential of blockchain in healthcare is clear: secure, immutable, and accessible medical records, tracking of medical supplies to prevent counterfeits from entering the market, improved patient care, secure payments and smart contracts, and accuracy of clinical trials. As the technology matures, its applications for the healthcare sector will improve:
- storage of patient medical records, ensuring data security, immutability, and accessible to only those who are authorized to access it,
- supply chain tracking of drugs to prevent counterfeit drugs from entering the market ensuring they are safe and authentic,
- patient care and reduce the risk of medical errors,
- management of clinical trials to speed up the development of new drugs and treatments.
Blockchain can further be used:
- for storing and managing patient consent records to facilitate medical procedures and ensure that patients are fully informed about the risks or benefits of treatment before giving their consent,
- for payments with greater convenience and reduced banking fraud.
Blockchain in Logistics
As the global logistics market continues to surge, reaching a value of $4,730 billion in 2018, the number of manufacturers, suppliers, and third-party intermediaries involved is increasing rapidly. This surge has projected a CAGR of 4.9 percent, leading to a predicted market value of $6,300 billion by 2023.
In order to keep up with the rising complexity of modern-day global supply chains and manage the increasing digitalization and data utilization, companies are turning to blockchain technology. Not only does this technology provide a competitive edge but can also help to address security and transparency concerns, increase efficiency and accuracy in operations, supply chain visibility and traceability.
Tracking the movement of goods and services through the entire supply chain (from the initial supplier to the end customer):
- provides permanent visibility and transparency,
- improved coordination of activities and decision-making through real-time audits.
By streamlining the process of exchanging data and payments, it can reduce:
- paperwork,
- the need for manual verification,
- and costs.
Automatization of inventory:
- through self-executed processes by using smart contracts,
- reduce costs and improve customer service.
Ensuring product authenticity:
- by establishing ‘single version of truth’,
- to protect consumers from counterfeit goods.
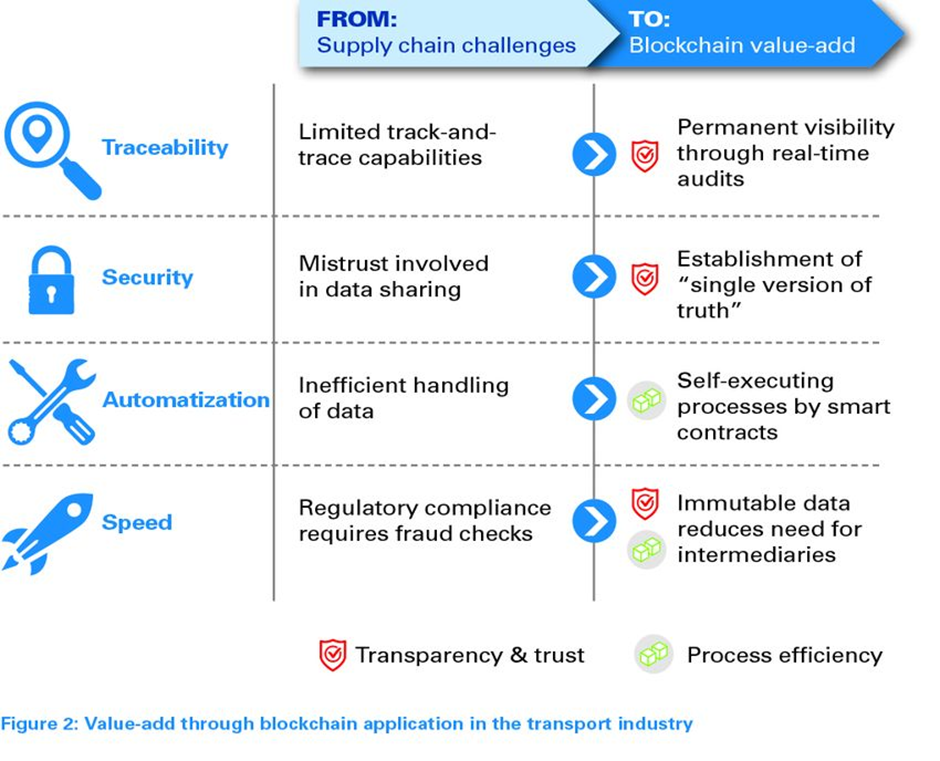
Source: ARTHUR LITTLE
Blockchain And Digital Identity In Different Industries
A new approach to digital identity management is emerging that is upending the current reliance on centralized authorities. Instead of relying on governments, financial institutions, or social media platforms, this approach focuses on decentralized identity management.
By allowing users to store and share their personal information securely, blockchain-based digital identities provide a wide range of advantages over traditional identification methods. Security is enhanced by the decentralized, tamper-proof storage of personal data, while privacy is improved through user control. Interoperability is facilitated by the ability to interchange information across organizations, and efficiency is increased by eliminating the need for intermediaries.
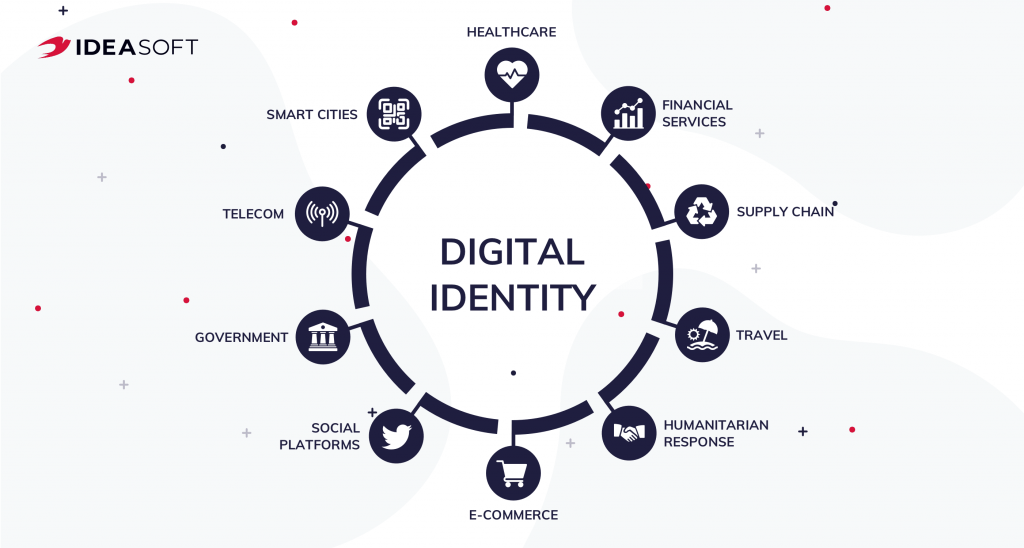
Source: IDEASOFT
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Heading For Mainstream Adoption
The cryptocurrency market has crossed a major milestone, with its total market capitalization surpassing $1 trillion – a value driven by growing acceptance of digital currency among U.S. retailers, with 75% of them saying that they plan to accept cryptocurrency payments within the next two years.
This could pave the way for a much larger-scale adoption of crypto, making it an increasingly mainstream payment method. Market watchers will be keeping a close eye on the data to assess the effects of this recent development.
Source: https://twitter.com/Cointelegraph
Blockchain in Layman’s Terms
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger of transactions, which are recorded and verified by a network of computers. This network is made up of nodes (computers that have a copy of the ledger). Each node is connected to other nodes in the network, allowing them to communicate and verify transactions. This allows for a secure, reliable way to keep track of information.
By creating a “block” of data that is then added to a chain of blocks, forms a chain of records that’s more secure and tamper-proof than traditional methods of storing data – ideal for purposes such as tracking financial transactions, managing digital identities, or maintaining records of ownership.
In addition to its secure nature, blockchain technology also offers transparency, allowing anyone with access to the chain of records to view the data stored in the blocks. This means that blockchain-based systems can be used to track and monitor transactions or assets in a secure and transparent way.

